What is a Cloud Client?
A cloud client is a hardware device or software used to access a cloud service. Computer systems, tablets, navigation devices, home automation devices, mobile phones and other smart devices, operating systems, and browsers can all be cloud clients.
Cloud clients have the basic processing and software capabilities needed to access specified cloud services. A cloud client is essential to accessing cloud services, but may also be completely functional without those services. There are three main service models of cloud computing: SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS.
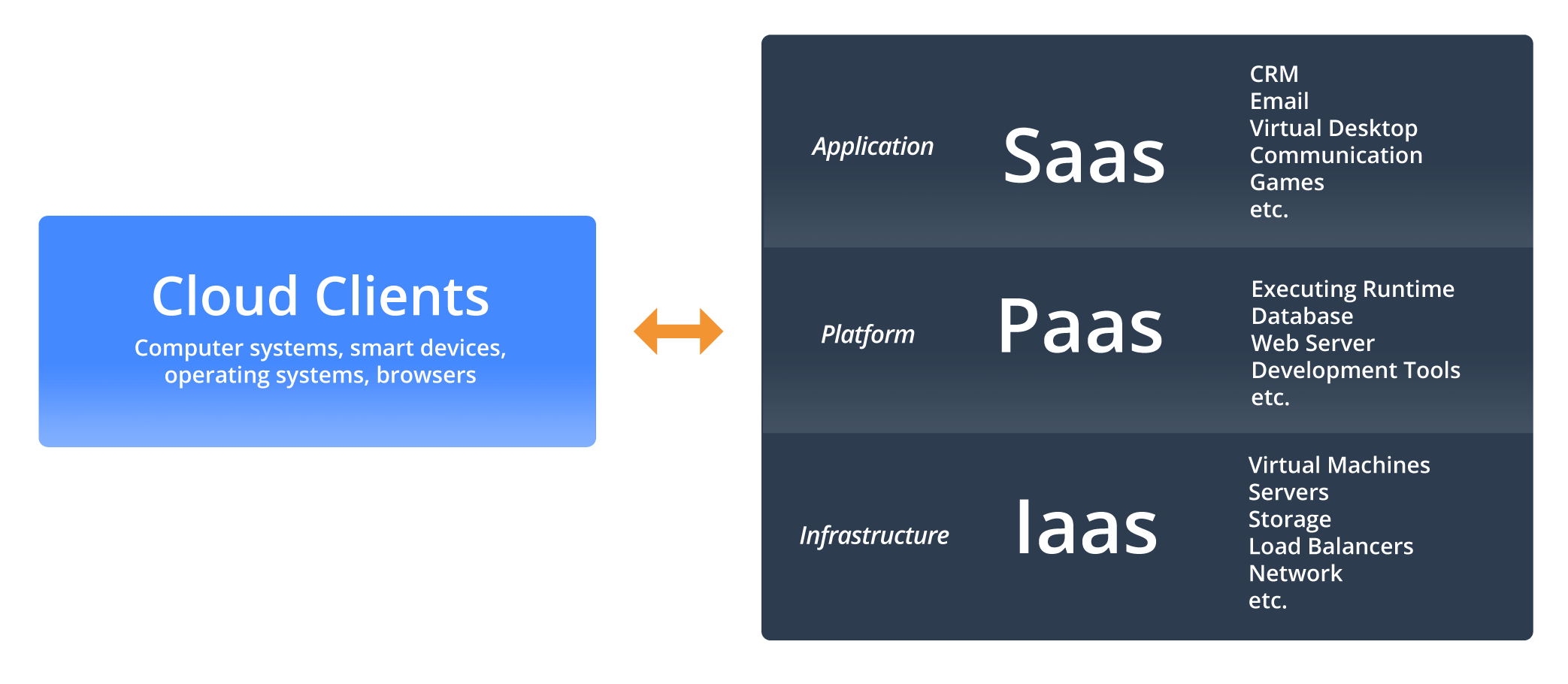
SaaS
Otherwise known as Software as a Service, SaaS is a cloud-based method of providing software to users. This type of software is licensed on a subscription basis and hosted in the cloud. Users can log into and use a SaaS application from any compatible device over the internet. Google Drive, Dropbox, and Salesforce are all examples of SaaS.
PaaS
Platform as a Service, also known as PaaS, is similar to SaaS only instead of providing software, PaaS provides a platform for software creation. With PaaS, developers are provided with a framework that they can use to create and build customized applications. Examples include Windows Azure, Google App Engnine, or OpenShift.
IaaS
Infrastructure as a Service delivers cloud computing infrastructure such as servers, networks, operating systems, and storage. Through a dashboard or an API, IaaS gives businesses complete control of the same technologies that a traditional data center provides without the need to physically maintain or manage those resources.
How Do Users Access Cloud Services?
Users securely access cloud services by connecting with cloud client devices such as desktop computers, laptops, tablets and smartphones. Some cloud clients rely on cloud computing for all or a majority of their applications and may be essentially useless without their cloud services. Examples of these types of cloud clients are thin client systems, which are computers that store their resources and memory on a central server instead of a localized hard drive, or browser-based devices such as Chromebooks. You can see cloud clients in action when visiting a medical office, watching your children use virtual classrooms and even when dining out in restaurants.
Many cloud applications do not require users to install specific software on the cloud client. In most cases, a secure web browser is all that is needed for interacting with the cloud application. Web user interfaces such as HTML5 can achieve a similar or even better user experience as native applications. Some cloud applications, however, support specific client software dedicated to these applications (e.g., virtual desktop clients and most email clients).
Though it is increasingly more common to access resources through a web browser instead of through installed software, older legacy software applications can still be accessed and used through cloud services. These older yet critically important programs can continue to be delivered via a screen-sharing solution. This enables clients to continue to access these programs until their organization can make the appropriate change or upgrade to either the best new version or more technically robust program.
How Cloud Services Can Benefit Your Company
Cloud services provide companies with flexibility to move into new solutions, allowing them to stay abreast or ahead of their marketplace. Adoption of cloud services also allows companies to work on their own time table regarding the use of legacy applications that are vital to the company.
You might also like
- QuickBooks in the Cloud: The Sky’s the Limit
- Database Cloud Services in Orange County: Scale at Will
- Distinguishing Between Public, Hybrid, & Private Cloud Solutions
- Quickbooks Cloud Hosting: How to Lower your IT Budget
- How Secure Cloud Technology Mitigates DDoS Attacks
- Suggested Responses to Recent AWS Cloud Outages from Industry Experts
- Creating Cloud Solutions That Benefit Your Company and Streamline Your Work Process
- Private Cloud as a Service
- What is a Community Cloud?
- Private Cloud vs. Virtualization
- Infrastructure as a Services (Iaas)
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)


