Defining Cloud Computing
Cloud Computing is a metaphor used by Technology or IT Services companies for the delivery of computing requirements as a service to a homogeneous community of end-recipients.
The term cloud theoretically signifies abstraction of technology, resources and its location that are very vital in building integrated computing infrastructure (including networks, systems & applications). All Cloud computing models rely heavily on sharing of resources to achieve coherence and economies of scale similar to a utility (like an electrical power grid) over a network (typically the Internet).
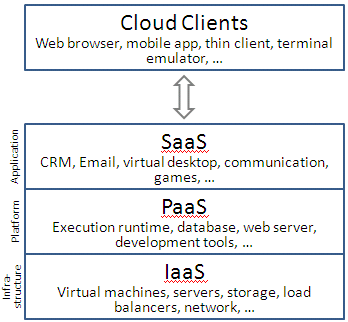
Cloud computing entrusts services (typically centralized) with a user’s data, software and computation on a published application programming interface (API) over a network. It has considerable overlap with software as a service (SaaS).
End users access cloud based applications through a web browser or a light weight desktop or mobile app while the business software and data are stored on servers at a remote location. Cloud application providers strive to give the same or better service and performance than if the software programs were installed locally on end-user computers.
At the foundation of cloud computing is the broader concept of infrastructure convergence (or Converged Infrastructure) and shared services. This type of data centre environment allows enterprises to get their applications up and running faster, with easier manageability and less maintenance, and enables IT to more rapidly adjust IT resources (such as servers, storage, and networking) to meet fluctuating and unpredictable demands of businesses.